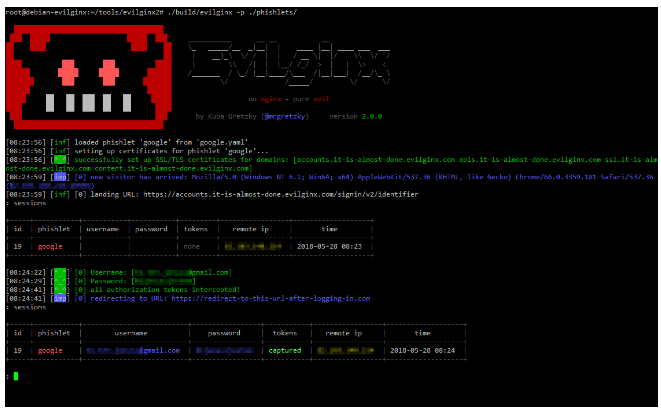
Website spoofing is the creation of a fake website that poses as a legitimate website, typically of a well-known company or organization.
A spoofed website copies the victim’s content and style to a T, making differentiating between the original and replica site nearly impossible. Spoofed websites are mostly used for stealing credentials, sensitive information, or delivering malware to the host device.
How Website Spoofing Poses Risks to Your Business
Spoofed websites can pose significant risks to businesses, including:
- Reputational damage
- Loss of customer trust
- Financial losses due to fraud and identity theft
- Disruption to business operations while dealing with the threat
To protect against website spoofing, it is important to regularly monitor your website and ensure that it is properly secured against attacks. Additionally, it is recommended that businesses educate employees and customers on how to identify and avoid spoofed websites.
How You Can Protect Users From Website Spoofing Attacks Targeting Your Domain
Protecting users from falling victim to website spoofing attacks targeting your domain requires a multilayered approach targeting the variety of spoofing methods and vulnerability points for any given domain. Organizations can hold mandatory employee training to reduce the risk of employee phishing attacks, but that only targets a piece of the problem.
Protecting your users from website spoofing involves consistent domain monitoring, and robust security measures to make it difficult for bad actors to generate replica domains..
These 4 prevention measures can help reduce user risk of falling victim to a website spoofing attack, and in turn protect your organization’s reputation and business continuity.
- Domain Name System (DNS) Security Extensions (DNSSEC): DNSSEC adds an extra layer of security to DNS by digitally signing the DNS records, making it more difficult for attackers to manipulate them.
- Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) Certificate: An SSL certificate helps encrypt the data transmitted between the website and users, and authenticates the website’s identity.
- Email Authentication: Implement email authentication protocols like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC to prevent spoofed emails from malicious domains and containing compromised links from being delivered to your customers.
- Regular Software Updates: Regularly update your website software, including the content management system (CMS), plugins, and themes, to patch any vulnerabilities that might be exploited by attackers.
- Digital Risk Protection Platform: Monitor your domain against threats and infringements with a digital risk protection solution that does detection and takedown of active phishing and scam sites.
Gain insight into current threats and domain risks targeting your network with a free Domain Risk Report & Acquisition Analysis.
What Tools Are Available To Help Protect Employees From Accessing Spoofed Sites?
There are various tools available to help protect employees from visiting spoofed websites and compromising personal and company data:
- Firewalls: A firewall can help prevent employees from accessing spoofed versions of websites by blocking malicious traffic and monitoring incoming and outgoing data.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): An IDPS can detect and prevent website spoofing by monitoring network traffic for signs of malicious activity.
- Anti-virus and Anti-malware Software: Anti-virus and anti-malware software can help protect employees from falling victim website spoofing by detecting and removing malicious software that can be used to create fake websites.
- Website Authentication Tools: Tools like SSL certificates and DNSSEC can be used to verify the authenticity of a website and help prevent them from ever getting in front of employees.
- Web Application Firewalls (WAFs): A WAF can help prevent website spoofing by monitoring and blocking malicious traffic to your website, including traffic from spoofed websites.
- Email Filtering Solutions: Email filtering solutions can help prevent email-based attacks on employees, including phishing attempts that use spoofed websites.
It’s important to use a combination of these tools to provide a comprehensive defense against website spoofing. Continuous domain monitoring technology, like Bolster’s Domain Monitoring Service enables organizations to effectively monitor for domain threats, lookalikes, and fake sites without active work from their internal team. Bolster’s technology can scan millions of network data points every day to prevent spoofing sites from targeting employees, and customers.
Additionally, cyber hygiene best-practices, like regularly updating your security software, performing backups, and regularly monitoring your website and network can help reduce the risk of a successful spoofing attack.
Is Website Spoofing The Same As Phishing?
Website spoofing is similar to phishing, but come at a slightly different scale in terms of protecting against them.
Phishing is a type of social engineering attack that uses emails, phone calls, or fake websites to trick individuals into providing sensitive information such as login credentials, credit card numbers, or other personal information. Website spoofing is one of the methods used in phishing attacks, where a fake website is created to mimic the appearance of a legitimate website in order to trick users into entering their sensitive information.
In other words, phishing encompasses website spoofing, as well as other types of social engineering attacks. Both website spoofing and phishing are malicious tactics used by attackers to steal sensitive information, but phishing is a wider term that encompasses different types of attacks, while website spoofing specifically refers to creating fake websites.
Learn more about the current state of phishing throughout the digital economy, and how your organization can proactively defend against attacks.
Is Website Spoofing The Same As Typosquatting?
Website spoofing is not exactly the same as typosquatting. Typosquatting, also known as URL hijacking, is a type of cyber attack in which an attacker creates a fake website with a similar URL to a legitimate website.
The fake website is often used to steal sensitive information, install malware, or display advertisements.
The main difference between typosquatting and website spoofing is that where typosquatting involves creating a fake website with a similar URL to the legitimate website, website spoofing involves creating a fake website that mimics the complete look and feel of the legitimate website.
In typosquatting, the attacker hopes that users will mistype the URL of the legitimate website and end up on the fake website accidently. In website spoofing, the attacker creates a fake website that looks very similar to the legitimate website, in the hopes of tricking users into entering sensitive information.
Is Website Spoofing The Same As Click Fraud?
To put it simply, website spoofing is not the same as click fraud.
Click fraud is a type of online fraud in which an attacker uses automated software to generate fake clicks on advertisements in order to artificially increase the number of clicks and inflate the cost of the advertisement. This can be done for financial gain, as the attacker may receive a commission for each click, or to harm the advertiser by draining their advertising budget.
Both click fraud and website spoofing are malicious tactics used to steal sensitive information or harm online businesses, but click fraud involves generating fake clicks on advertisements, while website spoofing involves creating a fake website that mimics a legitimate website.
What Techniques do Cybercriminals Use To Deceive Users With Spoof Websites?
Some of the most common techniques cybercriminals use to spoof websites include:
URL Masking
URL masking, also known as URL cloaking, is a technique used to hide the true URL of a website behind a different URL. This technique is often used to make it appear as though a website is hosted on a different domain, or to simplify a long and complicated URL.
URL masking can be used for both legitimate and malicious purposes. For example, a company may use URL masking to present a branded URL for its affiliate program, shorten a long URL, or to redirect users from an old website to a new website without breaking links. On the other hand, URL masking can also be used by cybercriminals to hide the true location of a phishing or malware-laden website.
It’s important to be cautious when clicking on links that are masked. It’s always a good idea to hover over the link to see the true URL before clicking on it, and to verify the authenticity of the website by checking the SSL certificate.
Homograph Attack
A homograph attack, also known as an IDN (Internationalized Domain Name) homograph attack, is a type of phishing attack that uses visually similar characters from different scripts (such as Latin and Cyrillic) to create a fake URL that looks similar to a legitimate URL.
For example, in a homograph attack the attacker may create a fake website using characters that look similar to Latin characters, but are actually from a different script. The letter “a” in Latin script could be replaced with the Cyrillic character “а”, which looks very similar to the Latin character. This can create a fake URL that looks very similar to a legitimate URL.
Homograph attacks can be particularly dangerous because they can be used to trick users into entering sensitive information on a fake website, or to spread malware. It’s important to be cautious when entering sensitive information online, and to verify the authenticity of a website by checking the SSL certificate and looking for other signs of security.
It’s also a good idea to use a browser that supports Punycode, which is a standardized representation of non-ASCII characters that can help prevent homograph attacks.
What Is The Result of Website Spoofing Attacks?
Cybercriminals perform website spoofing attacks for a variety of reasons, and often can result in many detrimental impacts for organization’s and their data, including:
- Malware Distribution: Website spoofing can also be used to distribute malware, by tricking users into downloading malicious software from a fake website.
- Click Fraud: Another reason for website spoofing is to carry out click fraud, where fake traffic is generated to a website to artificially inflate its advertising revenue.
- Brand Impersonation: Website spoofing can also be used to impersonate a brand and spread false information, or to damage the reputation of a brand.
- Financial Gain: Hackers who gain access to personal information and company data through website spoofing can exploit the information for financial gain, whether through holding data for ransom or forcing organization’s to pay to recover business operations.
In Summary
Website spoofing attacks are carried out by cybercriminals to steal sensitive information, spread malware, make money from click fraud, or damage a brand. It’s important to be cautious when visiting websites and to verify the authenticity of a website by checking the SSL certificate and looking for other signs of security.
Bolster’s automated digital risk monitoring and protection technology can prevent website spoofing from impacting your organization by actively scanning domain data using best-in-class mapping technology. Bolster offers a hands-free approach to spoofing detection, and will alert your team to threats and automate domain takedowns without manual input needed.
Learn more about how Bolster can help your organization combat website spoofing with an automated approach.